

Summer Astro Calendar
– June, July, August 2025
TOP TEN SKYGAZING PICKS
June 2 – Hercules Globular Cluster, M13, overhead at midnight. Binocular viewing
June 26 – Mercury highest altitude in evening sky
June 27 – June Bootid Meteor shower
July 16 – close approach Moon, Saturn, Neptune
July 20 – close approach Moon and M45.
July 21 – Conjunction of Moon and Venus pre-dawn
Aug. 1 – Venus at highest altitude in morning sky
Aug. 12 – Conjunction Venus and Jupiter. Conjunction of Moon and Saturn. Peak of Perseid meteor shower
Aug. 21 – Mercury highest altitude in morning sky
SUMMER PLANET VISIBILITIES
 |
Mercury: Evening – June and early July. West after sunset. Morning – August. |
 |
Venus: Morning – June, July, and August |
 |
Mars: Evening – June and July |
 |
Jupiter: Morning – late July and August |
 |
Saturn: Morning – June, July, and August |
Moon Phases Key
New Moon  First Quarter
First Quarter  Full Moon
Full Moon  Third Quarter
Third Quarter 
Moon Phases
| June | 2:  |
11:  |
18:  |
25:  |
|
| July | 2:  |
10:  |
17:  |
24:  |
|
| August | 2:  |
9:  |
16:  |
23:  |
31:  |
WHAT’S UP?
Annual Perseid Meteor Shower
The peak of the meteor shower is August 12. Although the waning gibbous Moon will bring brightness to the evening, dimming some of the famous streaks of light, there will be more treasures to observe. Brilliant Venus and Jupiter will be in conjunction in the constellation Gemini. Saturn and the Moon will be in conjunction near Pisces. Added treat, a small telescope will bring nearby Neptune into view.
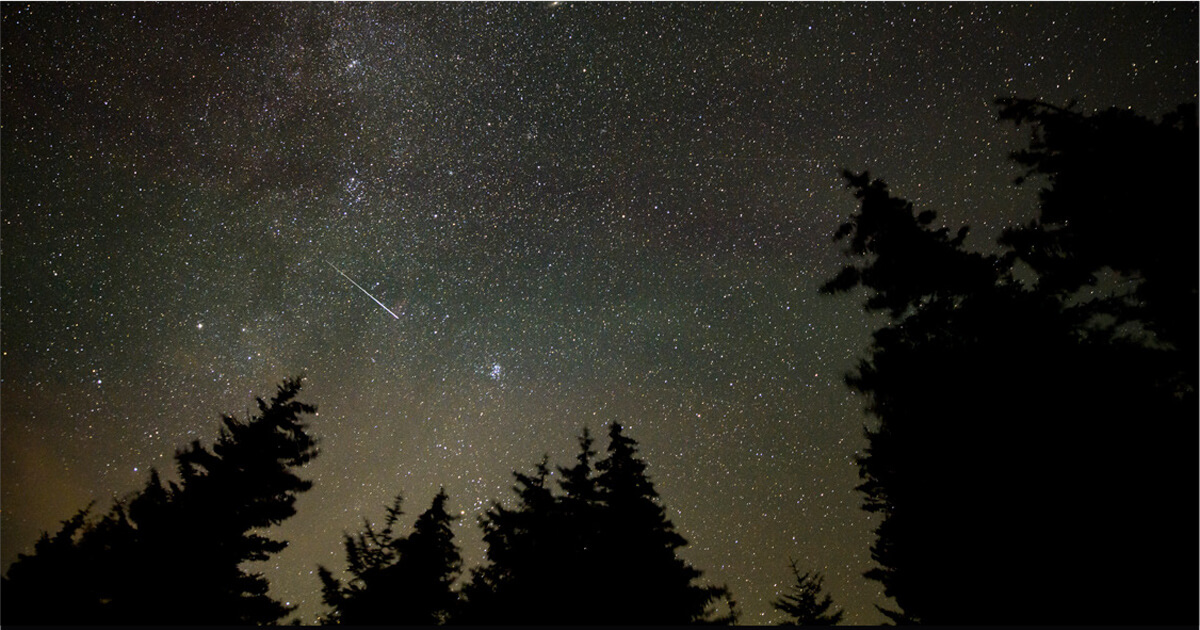

Image credit: NASA, Bill Ingalls
SPACE NEWS:
At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, rockets routinely lift off from famous launch pads. As space missions aim to explore cosmic mysteries, NASA’s surrounding wildlife preserve aims to protect over 1,500 types of plants and animals, one of which once lived among dinosaurs. The American Horseshoe Crab still roams seashores today. Strong indicators of a balanced ecosystem, NASA’s preserve researchers study the horseshoe crab for its contribution to wildlife survival. These resilient creatures even benefit humans. Their blue, copper-based blood was found useful in detecting types of bacterial contamination.
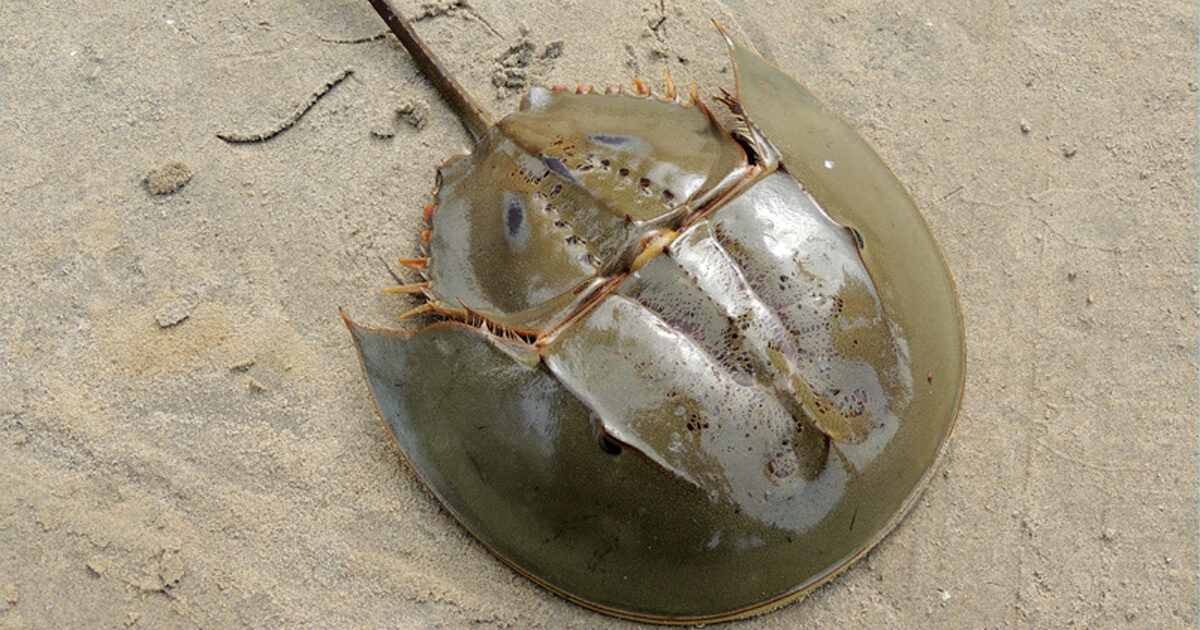

Image credit: Shubham Chatterjee
Star Chart (PDF) 

How do I use the star chart?
Hold it out in front of you with the direction you’re facing at the bottom of the chart. It works even better if you hold it above your head and look up at it.
Why are east and west switched?
They are only switched because you’re used to looking at maps of the ground. Hold it above your head, and you’ll see the directions line up just right.

